Prompt Strategy
The AutoDev Prompt Generation Strategy is the core functionality of AutoDev, which can generate optimal code suggestions based on your code context.

Typically, a prompt corresponding to an instruction consists of the following five components:
- Action type. For example:
Code complete,Translate to Kotlin, etc. - Language context (combined with specifications). For example: specifications corresponding to
Java,Kotlin,Python. - Technology stack context (combined with specifications). For example: specifications for Controller, Service, Repository.
- Relevant context (ClassProvider). For example: current file, current directory, current project, all files in the current project.
- Code (PsiElement). Current code.
Different languages implement ContextPrompter through their own modules, such as JavaContextPrompter, KotlinContextPrompter, etc.
Prompt Architecture
Therefore, AutoDev adopts a modular architecture inspired by Intellij Rust and JetBrains AI Assistant, as shown in the following diagram:
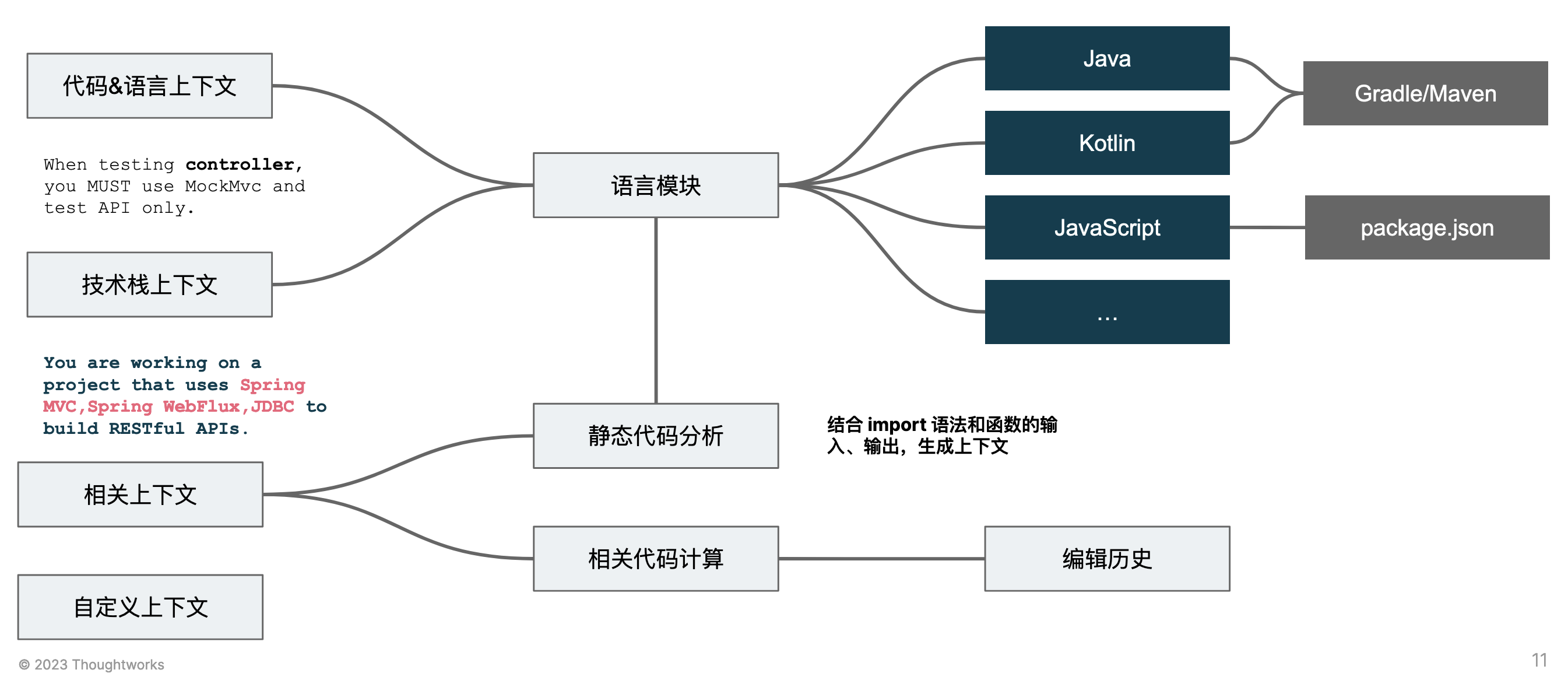
Each language module implements the corresponding language context and technology stack context based on abstract interfaces. This requires reading dependency-related information such as gradle, maven, package.json, etc.
Relevant Context
AutoDev provides the following types of relevant context:
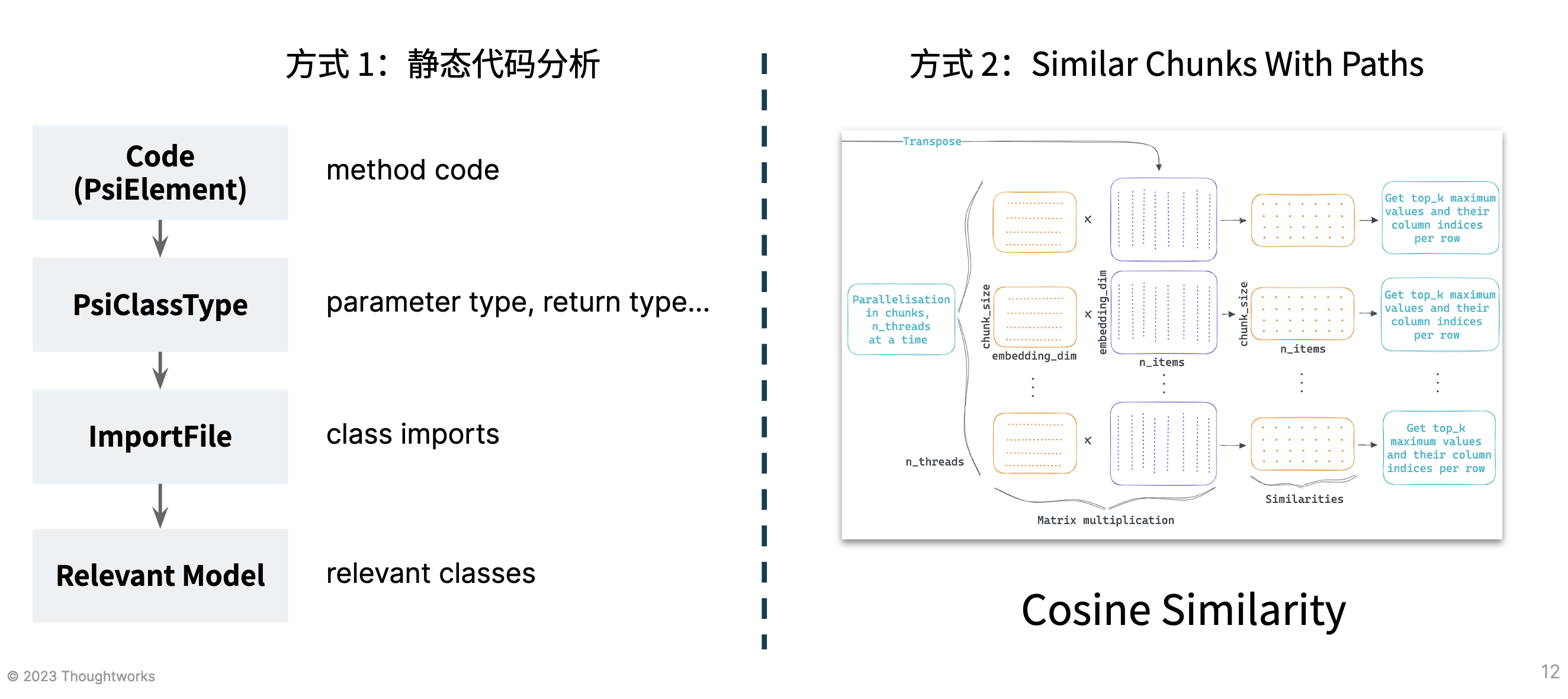
- Static code analysis approach: Generates corresponding context information by combining import syntax and function input/output.
- Corresponding implementation class: [JavaContextPrompter]
- Cosine Similarity calculation for code chunk similarity among the 20 most recently opened files. This is one of the implementation methods used by GitHub Copilot and JetBrains AI Assistant.
- Corresponding implementation class: [SimilarChunksWithPaths]
Dual-Prompt for Hidden Details
In AutoDev, complex prompts are implemented through two separate prompts, as shown below:
abstract class ContextPrompter {
open fun displayPrompt(): String = ""
open fun requestPrompt(): String = ""
...
}
displayPrompt: The prompt displayed to users, e.g.,Code complete,Translate to Kotlin.requestPrompt: The prompt sent to AI services, e.g.,Code complete:\n${METHOD_INPUT_OUTPUT}\n${SPEC_controller}\n\n${SELECTION}.
Depending on the scenario, certain details (such as related code chunks, input/output) may be hidden in the user-facing prompt.